The decline is positive, as overusing antimicrobials in animals can create drug-resistant bacteria, which can lead to human harm.
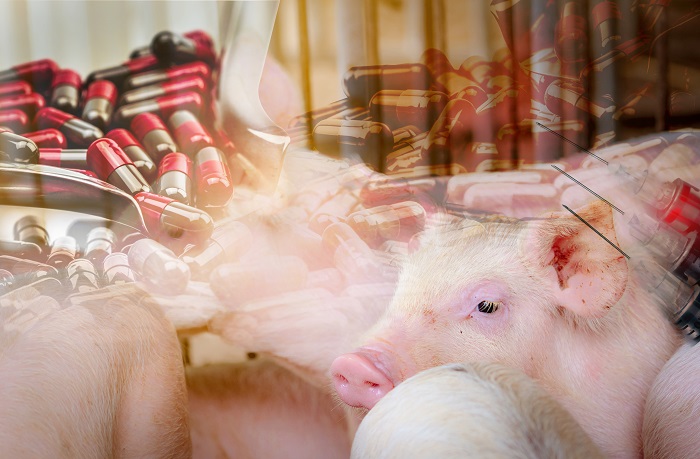

After decades of growth, the use of antimicrobials including antibiotics in livestock peaked in 2013 and then dropped by nearly a third by 2020, finds a major new study led by University College London (UCL) researchers.
The decline is positive, as overusing antimicrobials in animals can create drug-resistant bacteria, which can lead to human harm.
However, despite this trend, the study also found that richer developed countries continue to drive demand for antimicrobial-heavy products by importing large quantities of foods and products from emerging economies, that still use farm with high-levels of antimicrobials.
The research, published in Nature Sustainability, is the most detailed analysis yet of how antimicrobials are used in farming and manufacturing worldwide – and how international trade spreads that impact.
It looked at data from 2010 to 2020 to calculate each country’s ‘antimicrobial footprint’, similar to a carbon footprint, showing how much is used to make the products we consume.
Main findings:
|
Antimicrobials – including antibiotics – are widely used in livestock such as cattle, pigs and poultry to prevent disease and boost growth. But overusing them can create drug-resistant bacteria, which already cause around 700,000 deaths a year worldwide.
Cutting use is vital to protect human health. Their use in livestock accounts for about 73% of global consumption of all antimicrobials.
While many developed countries have reduced antimicrobial use at home, they often import products from countries where use is still high – effectively outsourcing the problem.
Between 2010 and 2020, the share of antimicrobials used for internationally traded goods rose from 16% to 20%. Surprisingly, about half of this was for non-food items like clothing, chemicals and electronics, which rely on animal-derived materials.
Emerging economies such as India and Indonesia have seen antimicrobial use rise, partly to meet export demand. India’s footprint grew by 16% over the decade.
Senior author Dr Heran Zheng of UCL Bartlett School of Sustainable Construction said: “The overuse of antimicrobials in livestock is a serious health concern, posing a potential global health threat. The decline in use in recent years is promising and shows that government regulation and intervention can be effective. Our research can help inform future guidance for their usage.”
Subscribe now to the technical pig magazine
AUTHORS

Bifet Gracia Farm & Nedap – Automated feeding in swine nurseries

The importance of Water on pig farms
Fernando Laguna Arán
Microbiota & Intestinal Barrier Integrity – Keys to Piglet Health
Alberto Morillo Alujas
Impact of Reducing Antibiotic use, the Dutch experience
Ron Bergevoet
The keys to successful Lactation in hyperprolific sows
Mercedes Sebastián Lafuente
Addressing the challenge of Management in Transition
Víctor Fernández Segundo
Dealing with the rise of Swine Dysentery
Roberto M. C. Guedes
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae – What are we dealing with?
Marcelo Gottschalk
The new era of Animal Welfare in Pig Production – Are we ready?
Antonio Velarde
Gut health in piglets – What can we do to measure and improve it?
Alberto Morillo Alujas
Interview with Cristina Massot – Animal Health in Europe after April 2021
Cristina Massot
Differential diagnosis of respiratory processes in pigs
Desirée Martín Jurado Gema Chacón Pérez